ISSUE1614
- Mark Abramowicz, M.D., President: no disclosure or potential conflict of interest to report
- Jean-Marie Pflomm, Pharm.D., Editor in Chief: no disclosure or potential conflict of interest to report
- Brinda M. Shah, Pharm.D., Consulting Editor: no disclosure or potential conflict of interest to report
- F. Peter Swanson, M.D., Consulting Editor: no disclosure or potential conflict of interest to report
- Michael Viscusi, Pharm.D., Associate Editor: no disclosure or potential conflict of interest to report
- Discuss the efficacy and safety of baricitinib for treatment of COVID-19.
- Mechanism of Action
- Clinical Study
- Adverse Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Dosage, Administration, and Cost
- Availability
- Conclusion
- References
Table
The oral Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor baricitinib (Olumiant – Lilly) has been granted an FDA Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for treatment of confirmed or suspected COVID-19 in hospitalized patients ≥2 years old who require supplemental oxygen, mechanical ventilation, or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO); the EUA requires that baricitinib be used in combination with the IV antiviral drug remdesivir (Veklury).1 Baricitinib has been available for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis since 2018.2 Remdesivir was recently approved by the FDA for treatment of COVID-19 in hospitalized patients ≥12 years old who weigh ≥40 kg; it is available under an EUA for treatment of other hospitalized patients.3
MECHANISM OF ACTION — JAK enzymes mediate signaling of proinflammatory cytokines, including interleukin-6. JAK inhibition by baricitinib may mitigate the response of these cytokines to SARS-CoV-2 and limit lung damage in patients with severe COVID-19. Baricitinib may also reduce the ability of the SARS-CoV-2 virus to enter human host cells.4
CLINICAL STUDY — Issuance of the EUA was based primarily on the results of a randomized, double-blind trial (ACTT-2; summarized in the FDA fact sheet) in 1033 hospitalized adults with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and either radiographic infiltrates, SpO2 ≤94% on room air, or a need for supplemental oxygen or mechanical ventilation. Patients received baricitinib 4 mg or placebo once daily for 14 days or until hospital discharge, in addition to IV remdesivir for up to 10 days.
Median time to recovery within 29 days after randomization, the primary endpoint, was shorter with baricitinib than with placebo (7 vs 8 days; p=0.03). Compared to those in the control group, patients taking baricitinib were also more likely to have an improvement in clinical status at day 15 (OR 1.3; 95% CI 1.0-1.6), and were less likely to meet the composite endpoint of death, progression to noninvasive or invasive mechanical ventilation, or (among those receiving oxygen or ventilation at baseline) worsening clinical status (OR 0.74; 95% CI 0.56-0.99). By day 29, 5.1% of patients who received baricitinib and 7.8% of those who received placebo had died; this difference was not statistically significant.5,6
ADVERSE EFFECTS — In ACTT-2, overall and serious adverse effects occurred less frequently in the baricitinib group than in the control group. Use of baricitinib for other indications has been associated with serious infections, thromboembolic events, hypersensitivity reactions, and hepatic enzyme elevations. In ACTT-2, there were more cases of venous thromboembolism and pulmonary embolism with baricitinib than with placebo (21 vs 16 and 5 vs 2, respectively); neither of these differences was statistically significant.5
DRUG INTERACTIONS — Strong OAT3 inhibitors such as probenecid can increase baricitinib exposure; the dosage of baricitinib should be reduced in patients taking a strong OAT3 inhibitor concurrently.
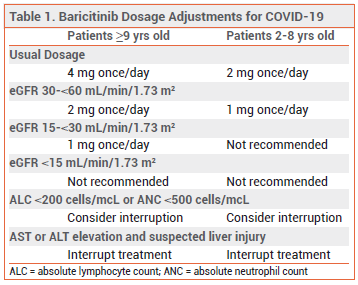
DOSAGE, ADMINISTRATION, AND COST — In the US, baricitinib is available in 1- and 2-mg tablets; the tablets can be taken orally or crushed and administered via gastrostomy or nasogastric tube. The authorized dosage for treatment of COVID-19 is 4 mg once daily in patients ≥9 years old and 2 mg once daily in children 2-8 years old. Recommended dosage adjustments and interruptions for renal impairment and laboratory abnormalities are summarized in Table 1. The optimal duration of baricitinib treatment for COVID-19 is unknown, but the FDA recommends that the drug be taken for 14 days or until hospital discharge, whichever is first.6 The cost for 14 days of treatment with baricitinib at the usual adult dosage is $2114.7
AVAILABILITY — A list of authorized distributors from which inpatient pharmacies can order baricitinib for use under the EUA is available at www.lillytrade.com.
CONCLUSION — The oral Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor baricitinib (Olumiant), used in combination with the IV antiviral drug remdesivir (Veklury), reduced median time to recovery by one day in patients who were hospitalized for COVID-19 and had radiographic infiltrates, SpO2 ≤94% on room air, or a need for supplemental oxygen or mechanical ventilation. Baricitinib increases the risk of venous thromboembolism and it is expensive.
- FDA News Release. Coronavirus (COVID-19) update: FDA authorizes drug combination for treatment of COVID-19. November 19, 2020. Available at: https://bit.ly/3lNvV4I. Accessed December 10, 2020.
- Baricitinib (Olumiant) for rheumatoid arthritis. Med Lett Drugs Ther 2018; 60:120.
- Remdesivir (Veklury) for COVID-19. Med Lett Drugs Ther 2020; 62:186.
- YC Tsai and TF Tsai. Oral disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and immunosuppressants with antiviral potential, including SARSCoV-2 infection: a review. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis 2020; 12:1.
- AC Kalil et al. Baricitinib plus remdesivir for hospitalized adults with COVID-19. N Engl J Med 2020 December 11 (epub).
- FDA. Fact sheet for health care providers. Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) of baricitinib. Available at: https://bit.ly/2JXpaA1. Accessed December 10, 2020.
- Approximate WAC. WAC = wholesaler acquisition cost or manufacturer's published price to wholesalers; WAC represents a published catalogue or list price and may not represent an actual transactional price. Source: Analysource® Monthly. December 5, 2020. Reprinted with permission by First Databank, Inc. All rights reserved. ©2020. www.fdbhealth. com/policies/drug-pricing-policy.