ISSUE1635
- Mark Abramowicz, M.D., President: no disclosure or potential conflict of interest to report
- Jean-Marie Pflomm, Pharm.D., Editor in Chief: no disclosure or potential conflict of interest to report
- Brinda M. Shah, Pharm.D., Consulting Editor: no disclosure or potential conflict of interest to report
- Michael Viscusi, Pharm.D., Associate Editor: no disclosure or potential conflict of interest to report
- Review the efficacy and safety of bamlanivimab and etesevimab together for post-exposure prophylaxis of COVID-19 infection and discuss the conditions that increase the risk for severe COVID-19 infection.
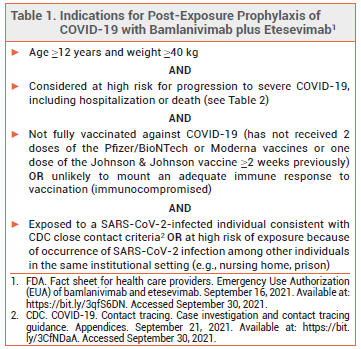
In February 2021, the FDA issued an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for the investigational monoclonal antibodies bamlanivimab and etesevimab (Lilly) for use together to treat mild to moderate COVID-19 in persons ≥12 years old who weigh ≥40 kg and are at high risk of progression to severe disease or hospitalization.1 The FDA has now expanded this EUA to allow use of the antibodies together for post-exposure prophylaxis of COVID-19 in such persons if they are not fully vaccinated against COVID-19 or are unlikely to have an adequate immune response to full vaccination and have been in close contact with a SARS-CoV-2-infected individual or are likely to be exposed to SARS-CoV-2 in the setting of an institutional outbreak (see Table 1).2 Bamlanivimab plus etesevimab is the second monoclonal antibody combination to receive an EUA for post-exposure prophylaxis of COVID-19; casirivimab plus imdevimab (REGEN-COV) was authorized earlier.3
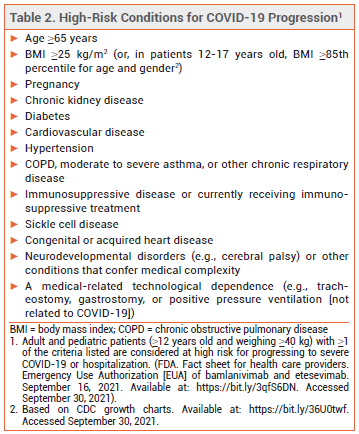
ELIGIBILITY — In May 2021, the FDA expanded the criteria by which a patient with COVID-19 can be considered at high risk for disease progression. All persons ≥12 years old who are overweight, pregnant, or have cardiovascular disease, hypertension, or chronic respiratory disease are now considered high-risk (see Table 2).4
CLINICAL STUDIES — In an unpublished double-blind trial (BLAZE-2 Part 1; summarized in the FDA Fact Sheet), 966 SARS-CoV-2-negative residents or staff of skilled nursing facilities where a confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection occurred were randomized to receive a single dose of bamlanivimab 2800 mg (without etesevimab) or placebo.
The risk of symptomatic COVID-19 within 8 weeks of randomization, the primary endpoint, was significantly lower in patients who received bamlanivimab than in those who received placebo in both the overall population (8.5% vs 15.2%; number needed to treat [NNT] 15.1; adjusted OR 0.43 [95% CI 0.28-0.68]) and the prespecified subgroup of nursing facility residents (8.9% vs 22.5%; NNT 7.4; adjusted OR 0.20 [95% CI 0.08-0.49]). There were no deaths due to COVID-19 in the bamlanivimab group versus 4 in the placebo group.2,5
No data on the use of bamlanivimab plus etesevimab for post-exposure prophylaxis of COVID-19 are available. Because the combination has greater antiviral activity than bamlanivimab alone, the FDA presumed it to be effective based on the results of BLAZE-2 Part 1. No clinical trials have compared bamlanivimab plus etesevimab with casirivimab plus imdevimab.
ADVERSE EFFECTS — Infusion-related reactions and anaphylaxis have been reported with use of bamlanivimab plus etesevimab.
VARIANTS — Bamlanivimab plus etesevimab is not active against the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2. The combination retains activity against the Delta variant of the virus.2
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION — The authorized dosage of bamlanivimab plus etesevimab for post-exposure prophylaxis is 700 mg of bamlanivimab and 1400 mg of etesevimab given as a single IV infusion as soon as possible after exposure to SARS-CoV-2. Patients should be monitored during the infusion and for at least 1 hour after its completion. Unlike REGEN-COV, bamlanivimab and etesevimab cannot be given by subcutaneous injection. Detailed instructions on preparation and administration of the antibodies are available in the FDA Fact Sheet.2
CONCLUSION — The FDA has authorized administration of the monoclonal antibodies bamlanivimab and etesevimab together for IV post-exposure prophylaxis of COVID-19 in certain high-risk persons. In a double-blind trial in SARS-CoV-2-negative residents and staff of nursing facilities in which a confirmed infection occurred, IV infusion of bamlanivimab alone significantly decreased the risk of symptomatic COVID-19 compared to placebo. The overall effectiveness of the two antibodies together for post-exposure prophylaxis remains to be determined. Bamlanivimab plus etesevimab retains efficacy against the Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2.
- An EUA for bamlanivimab and etesevimab for COVID-19. Med Lett Drugs Ther 2021; 63:49.
- FDA. Fact sheet for health care providers. Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) of bamlanivimab and etesevimab. December 22, 2021. Available at: https://bit.ly/3qfS6DN. Accessed January 6, 2022.
- Casirivimab and imdevimab (REGEN-COV) for post-exposure prophylaxis of COVID-19. Med Lett Drugs Ther 2021; 63:130.
- FDA News Release. Coronavirus (COVID-19) update: May 21, 2021. Available at: https://bit.ly/3fFoEUB. Accessed September 30, 2021.
- Lilly. What is the effect of bamlanivimab and etesevimab prevention treatment on COVID-19 symptoms? Medical information request response, September 23, 2021.