ONLY
ARTICLE
- Mark Abramowicz, M.D., President: no disclosure or potential conflict of interest to report
- Jean-Marie Pflomm, Pharm.D., Editor in Chief: no disclosure or potential conflict of interest to report
- Brinda M. Shah, Pharm.D., Consulting Editor: no disclosure or potential conflict of interest to report
- Michael Viscusi, Pharm.D., Associate Editor: no disclosure or potential conflict of interest to report
- Discuss the recent updates in COVID-19 vaccination and treatment recommendations.
The FDA has approved the oral Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor baricitinib (Olumiant) for treatment of COVID-19 in hospitalized adults who require supplemental oxygen, mechanical ventilation, or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).1 Baricitinib was previously available for this indication under an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA); it remains available under an EUA for use in children 2-17 years old hospitalized with COVID-19 who require oxygen support.2
CLINICAL STUDIES – FDA approval of baricitinib for treatment of COVID-19 was based on the results of two randomized, double-blind trials in hospitalized adults with COVID-19.
In one trial (ACTT-2), 1033 patients with radiographic infiltrates, SpO2 ≤94% on room air, or a need for supplemental oxygen or mechanical ventilation received baricitinib 4 mg or placebo once daily for up to 14 days while hospitalized, in addition to IV treatment with the antiviral drug remdesivir (Veklury) for up to 10 days. The median time to recovery within 29 days after randomization, the primary endpoint, was significantly shorter with baricitinib than with placebo (7 vs 8 days; rate ratio 1.16 [95% CI 1.01-1.32]). Compared to those in the control group, patients taking baricitinib were also more likely to have an improvement in clinical status at day 15 (OR 1.3 [95% CI 1.0-1.6]). The mortality rate by day 29 was lower in the baricitinib group, but this difference was not statistically significant (5.1% vs 7.8%; HR 0.65 [95% CI 0.39-1.09]).3
In the other trial (COV-BARRIER), 1525 patients with at least one elevated inflammatory marker received baricitinib 4 mg (2 mg in patients with a baseline eGFR of 30 to <60 mL/min/1.73 m2) or placebo once daily for up to 14 days while hospitalized, in addition to standard treatment (91% of patients were also receiving dexamethasone). The rate of disease progression or death by day 28, the primary endpoint, did not significantly differ between the baricitinib and placebo groups (27.8% vs 30.5%; HR 0.85 [95% CI 0.67-1.08]). The rate of all-cause mortality, however, was significantly lower in the baricitinib group (8.1% vs 13.1%; HR 0.57 [95% CI 0.41-0.78]; NNT 19.9), particularly in the subgroup of patients who required high-flow oxygen or noninvasive ventilation at baseline (17.5% vs 29.4%; HR 0.52 [95% CI 0.33-0.80]; NNT 8.4).4
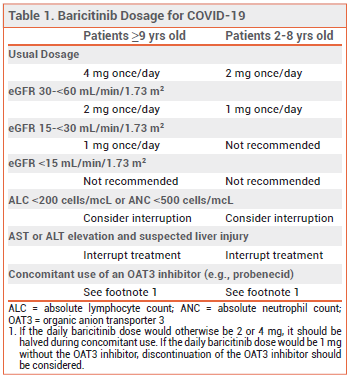
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION – The usual recommended dosage of baricitinib for treatment of COVID-19 in adults is 4 mg taken once daily while hospitalized for up to 14 days. Baricitinib tablets can be taken orally or crushed and administered via gastrostomy or nasogastric tube. Recommended dosage adjustments for renal impairment, laboratory abnormalities, and drug interactions are summarized in Table 1.
RECOMMENDATIONS – NIH guidelines on treatment of COVID-19 in hospitalized adults recommend giving baricitinib to patients who require high-flow oxygen or noninvasive ventilation and have rapidly increasing oxygen needs and systemic inflammation. Baricitinib should be coadministered with dexamethasone; remdesivir can also be given concomitantly.5
- FDA News Release. FDA roundup: May 10, 2022. Available at: https://bit.ly/3lkwftW. Accessed May 23, 2022.
- FDA. Fact sheet for health care providers. Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) of baricitinib. May 2022. Available at: https://bit.ly/2JXpaA1. Accessed May 23, 2022.
- AC Kalil et al. Baricitinib plus remdesivir for hospitalized adults with Covid-19. N Engl J Med 2021; 384:795.
- VC Marconi et al. Efficacy and safety of baricitinib for the treatment of hospitalised adults with COVID-19 (COV-BARRIER): a randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, placebocontrolled phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir Med 2021; 9:1407.
- NIH. COVID-19 treatment guidelines. Therapeutic management of hospitalized adults with COVID-19. February 24, 2022. Available at: https://bit.ly/3DfsFsJ. Accessed May 23, 2022.