ISSUE1429
The FDA is requiring new warnings about peripheral neuropathy in the labeling of all oral and injectable fluoroquinolones. The potential for this class of antibiotics to cause peripheral neuropathy was first identified more than 10 years ago and a warning was added to their labels in 2004. The new warnings are based on a recent review of the FDA’s Adverse Event Reporting System (AERS) database.1
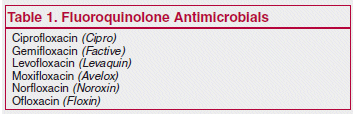
The onset of peripheral neuropathy can occur rapidly, often within a few days of starting a fluoroquinolone, and in some patients the disorder may be permanent. Symptoms include pain, tingling, burning, numbness, weakness, and change in sensation to touch, pain, and temperature in the arms and/or legs. If peripheral neuropathy develops in a patient taking a fluoroquinolone, the drug should be stopped and an antibacterial from a different class should be used instead.2
1. FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA requires label changes to warn of risk for possibly permanent nerve damage from antibacterial fluoroquinolone drugs taken by mouth or by injection. Available at http://www.fda.gov. Accessed November 1, 2013.
2. Drugs for bacterial infections. Treat Guidel Med Lett 2013; 11:65.
